电子发烧友
2151次浏览
高斯滤波和双边滤波在图像处理中都是常用的平滑滤波技术,但它们之间存在一些显著的区别。以下是两者之间的主要区别: 一、基本原理 高斯
2024-09-29 09:37
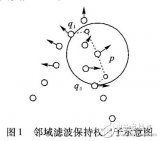
针对三维点云数据模型在去噪光顺中存在不同尺度噪声的问题,提出一种基于噪声分类的双边滤波点云去噪算法。该算法首先将噪声细分为大尺度和小尺度噪声,并使用统计滤波结合半径滤波
2018-01-05 10:51

前面发过中值、均值、高斯滤波的文章,这些只考虑了位置,并没有考虑相似度。那么双边滤波来了,既考虑了位置,有考虑了相似度,对边缘的保持比前几个好很多,当然实现上也是复杂很多。本文将从原理入手,采用Matlab与FPGA
2025-07-10 11:28
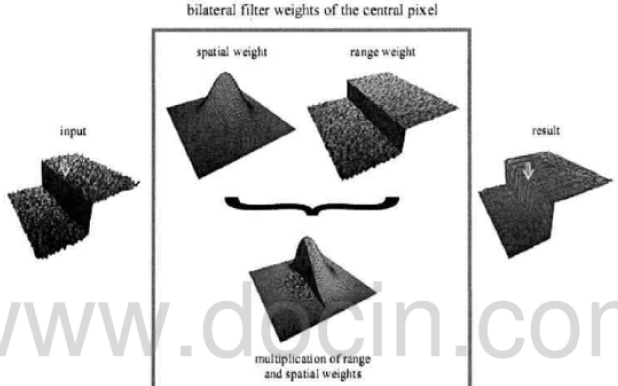
滤波是图像处理和计算机视觉中最基本的操作,高斯低通滤波是最常用的,其原理是邻域内像素值的加权平均。这种邻域内的平均会使一些边界被平均掉而使图像出现模糊,双边滤波正是为了
2018-12-21 09:53
双边滤波(Bilateral filter)是一种可以保边去噪的滤波器。之所以可以达到此去噪效果,是因为滤波器是由两个函数构成。一个函数是由几何空间距离决定
2018-06-29 08:19
%% output = bilateralFilter( data, edge, ...%edgeMin, edgeMax, ...%sigmaSpatial, sigmaRange, ...%samplingSpatial, samplingRange )%% Bilateral and Cross-Bilateral Filter using the Bilateral Grid.%% Bilaterally filters the image 'data' using the edges in the image 'edge'.% If 'data' == 'edge', then it the standard bilateral filter.% Otherwise, it is the 'cross' or 'joint' bilateral filter.% For convenience, you can also pass in [] for 'edge' for the normal% bilateral filter.%% Note that for the cross bilateral filter, data does not need to be% defined everywhere.Undefined values can be set to 'NaN'.However, edge% *does* need to be defined everywhere.%% data and edge should be of the greyscale, double-precision floating point% matrices of the same size (i.e. they should be [ height x width ])%% data is the only required argument%% edgeMin and edgeMax specifies the min and max values of 'edge' (or 'data'% for the normal bilateral filter) and is useful when the input is in a% range that's not between 0 and 1.For instance, if you are filtering the% L channel of an image that ranges between 0 and 100, set edgeMin to 0 and% edgeMax to 100.% % edgeMin defaults to min( edge( : ) ) and edgeMax defaults to max( edge( : ) ).% This is probably *not* what you want, since the input may not span the% entire range.%% sigmaSpatial and sigmaRange specifies the standard deviation of the space% and range gaussians, respectively.% sigmaSpatial defaults to min( width, height ) / 16% sigmaRange defaults to ( edgeMax - edgeMin ) / 10.%% samplingSpatial and samplingRange specifies the amount of downsampling% used for the approximation.Higher values use less memory but are also% less accurate.The default and recommended values are:% % samplingSpatial = sigmaSpatial% samplingRange = sigmaRange%function output = fBilateralFilter_ReviseVer( data, edge, edgeMin, edgeMax, sigmaSpatial, sigmaRange, ... samplingSpatial, samplingRange )if( ndims( data ) > 2 ), error( 'data must be a greyscale image with size [ height, width ]' );endif( ~isa( data, 'double' ) ), error( 'data must be of class "double"' );endif ~exist( 'edge', 'var' ), edge = data;elseif isempty( edge ), edge = data;endif( ndims( edge ) > 2 ), error( 'edge must be a greyscale image with size [ height, width ]' );endif( ~isa( edge, 'double' ) ), error( 'edge must be of class "double"' );endinputHeight = size( data, 1 );inputWidth = size( data, 2 );if ~exist( 'edgeMin', 'var' ), edgeMin = min( edge( : ) ); warning( 'edgeMin not set!Defaulting to: %f\n', edgeMin );endif ~exist( 'edgeMax', 'var' ), edgeMax = max( edge( : ) ); warning( 'edgeMax not set!Defaulting to: %f\n', edgeMax );endedgeDelta = edgeMax - edgeMin;% hl- span of range% hl- assign scale parameters in both spatial and range domainif ~exist( 'sigmaSpatial', 'var' ), sigmaSpatial = min( inputWidth, inputHeight ) / 16; fprintf( 'Using default sigmaSpatial of: %f\n', sigmaSpatial );endif ~exist( 'sigmaRange', 'var' ), sigmaRange = 0.1 * edgeDelta; fprintf( 'Using default sigmaRange of: %f\n', sigmaRange );endif ~exist( 'samplingSpatial', 'var' ), samplingSpatial = sigmaSpatial;endif ~exist( 'samplingRange', 'var' ), samplingRange = sigmaRange;endif size( data ) ~= size( edge ), error( 'data and edge must be of the same size' );end% parametersderivedSigmaSpatial = sigmaSpatial / samplingSpatial; % ??????????derivedSigmaRange = sigmaRange / samplingRange;paddingXY = floor( 2 * derivedSigmaSpatial ) + 1;paddingZ = floor( 2 * derivedSigmaRange ) + 1;% allocate 3D griddownsampledWidth = floor( ( inputWidth - 1 ) / samplingSpatial ) + 1 + 2 * paddingXY; % paddingXY - 控制延拓范围downsampledHeight = floor( ( inputHeight - 1 ) / samplingSpatial ) + 1 + 2 * paddingXY;downsampledDepth = floor( edgeDelta / samplingRange ) + 1 + 2 * paddingZ;gridData = zeros( downsampledHeight, downsampledWidth, downsampledDepth );gridWeights = zeros( downsampledHeight, downsampledWidth, downsampledDepth );% compute downsampled indices[ jj, ii ] = meshgrid( 0 : inputWidth - 1, 0 : inputHeight - 1 ); % hl- create the coordinats of xy-plane; jj - y coordinates of all pixels, ii - x coordinates of all pixels% ii =% 0 0 0 0 0% 1 1 1 1 1% 2 2 2 2 2% jj =% 0 1 2 3 4% 0 1 2 3 4% 0 1 2 3 4% so when iterating over ii( k ), jj( k )% get: ( 0, 0 ), ( 1, 0 ), ( 2, 0 ), ... (down columns first)%% Compute the downsampled coordinatesdi = round( ii / samplingSpatial ) + paddingXY + 1; % round: Round to nearest integer四舍五入dj = round( jj / samplingSpatial ) + paddingXY + 1;dz = round( ( edge - edgeMin ) / samplingRange ) + paddingZ + 1;%% hl - average sampling (box sampling)% perform scatter (there's probably a faster way than this)% normally would do downsampledWeights( di, dj, dk ) = 1, but we have to% perform a summation to do box downsamplingfor k = 1 : numel( dz ), % numel: Number of elements in an array dataZ = data( k ); % traverses the image column wise, same as di( k ) if ~isnan( dataZ),dik = di( k ); %取出坐标djk = dj( k );dzk = dz( k );gridData( dik, djk, dzk ) = gridData( dik, djk, dzk ) + dataZ;gridWeights( dik, djk, dzk ) = gridWeights( dik, djk, dzk ) + 1; endend% make gaussian kernelkernelWidth = 2 * derivedSigmaSpatial + 1;kernelHeight = kernelWidth;kernelDepth = 2 * derivedSigmaRange + 1;halfKernelWidth = floor( kernelWidth / 2 );halfKernelHeight = floor( kernelHeight / 2 );halfKernelDepth = floor( kernelDepth / 2 );[gridX, gridY, gridZ] = meshgrid( 0 : kernelWidth - 1, 0 : kernelHeight - 1, 0 : kernelDepth - 1 );gridX = gridX - halfKernelWidth;gridY = gridY - halfKernelHeight;gridZ = gridZ - halfKernelDepth;gridRSquared = ( gridX .* gridX + gridY .* gridY ) / ( derivedSigmaSpatial * derivedSigmaSpatial ) + ( gridZ .* gridZ ) / ( derivedSigmaRange * derivedSigmaRange );kernel = exp( -0.5 * gridRSquared );% convolveblurredGridData = convn( gridData, kernel, 'same' );blurredGridWeights = convn( gridWeights, kernel, 'same' );% divideblurredGridWeights( blurredGridWeights == 0 ) = -2; % avoid divide by 0, won't read there anywaynormalizedBlurredGrid = blurredGridData ./ blurredGridWeights;normalizedBlurredGrid( blurredGridWeights < -1 ) = 0; % put 0s where it's undefined% for debugging% blurredGridWeights( blurredGridWeights < -1 ) = 0; % put zeros back% upsample[ jj, ii ] = meshgrid( 0 : inputWidth - 1, 0 : inputHeight - 1 ); % meshgrid does x, then y, so output arguments need to be reversed% no roundingdi = ( ii / samplingSpatial ) + paddingXY + 1;dj = ( jj / samplingSpatial ) + paddingXY + 1;dz = ( edge - edgeMin ) / samplingRange + paddingZ + 1;% for p=1:inputHeight%for q=1:inputWidth%A{p,q}=[num2str(di(p,q)),' ',num2str(dj(p,q)),' ',num2str(dz(p,q))];%end;% end;% interpn takes rows, then cols, etc% i.e. size(v,1), then size(v,2), ...output = interpn( normalizedBlurredGrid, di, dj, dz ); % N-D data interpolation其中 第117,118,119行中的downsampledWidth,downsampledHeight,downsampledDepth为什么要加1?
2015-10-24 21:56
一种改进的增维型双边滤波的快速算法_李俊峰
2017-01-07 16:00
想用FPGA实现双边滤波算法,有懂得能说一下具体的实现步骤吗
2017-03-21 15:41
本帖最后由 lxzxj_chan 于 2015-10-23 12:07 编辑 这段代总体思路是什么,怎样实现双边滤波?%% output = bilateralFilter( data
2015-10-23 09:36
采用密度k_means和改进双边滤波的点云自适应去噪算法_郭进
2017-03-19 18:58